

Secondary hydrocele: The risk is very low (less than 1%) since dissection of the spermatic cord is done under a microscope. Lymphatic tissues are not severed or ligated. Their ligatures are responsible for the appearance of a hydrocele. It can be corrected later, if necessary.
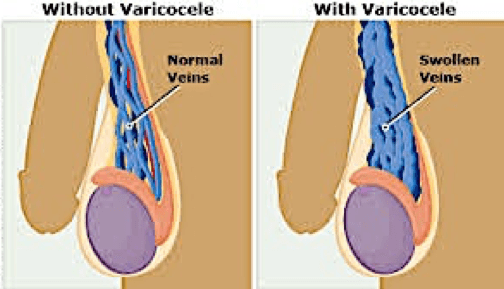
Persistent veins: It may have a persistence of dilated veins despite improved symptoms.
Recidivism: The risk of recurrence is low because of abnormal venous communications. Re intervention or embolization may be proposed.
Hematoma: A bruise is common, but a hematoma is rare. It may require drainage.
Infection: Wound infections are rare. Infected wounds can become hot, swollen, red, and painful, with significant drainage from the incision site, and patients may develop fever. If wounds become infected (usually 3 to 5 days after surgery), antibiotics may be needed.
Testicular atrophy: It is secondary to testicular ischemia since an arterial branch has been ligated It is exceptional after a varicocele cure by microscopy and micro-Doppler under inguinal. Spermatic arteries are usually all identified.
What are the implications of a varicocele cure by microscopy and micro-doppler under inguinal?
Why opt for an inguinal approach during a varicocele surgery?
Why use a microscope and a micro-doppler during subinguinal microsurgical varicocelectomy?
What are the reasons to perform a subinguinal microsurgical varicocelectomy ?
- Infertility.
- Left scrotal discomfort.
- Testosterone deficiency in older men.
- Dr Marois will take the time to assess the patient and determine if this surgery is needed or an option.
How is a varicocelectomy performed?
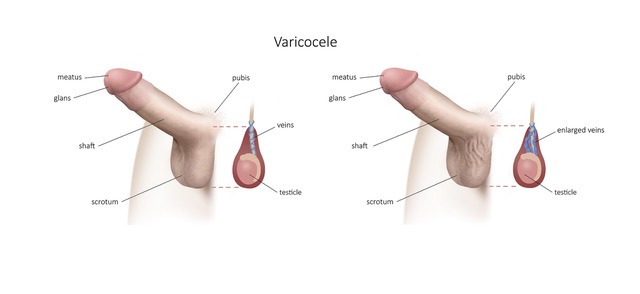
A short incision of 3 cm is made at the inguinal level to expose the spermatic cord. The spermatic veins are identified under the microscope. They are then ligated. A segment of vein is excised to reduce the risk of re-anastomosis.
A 3 mm micro-Doppler is introduced before the beginning of the fine dissection. The surgical area is copiously irrigated with a 1% Lidocaine solution to fight against vasospasm (although Papaverine dilution may also be used). Dr Marois will then start looking for the artery with the micro-Doppler probe. Once this has been identified, he will take special care to protect it and reconfirm its identity throughout the dissection. The vas deferens and its vascular bundle are then identified and, if possible, brought to the lateral or medial edge of the cord and excluded from the operative field. All lymphatics are identified and preserved to minimize the risk of postoperative hydrocele.
Irrigation of saline water is necessary during the procedure. The skin is closed by resorbable threads and surgical glue. Dressings are applied. The procedure can last about 90 minutes.
What are the results of a varicocele cure?
Fertility surgery: Several studies show that the number and motility of spermatozoa improves after varicocele surgery. Some studies suggest that couples with repaired varicocele are 30-50% more likely to become pregnant than couples without repaired varicocele.


