What is Infectious balanitis
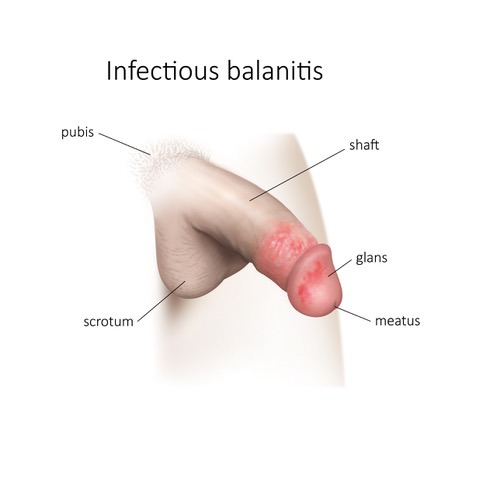
Balanitis (inflammation of the glans) and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the foreskin) infectious.
As specialists in penile disorders, Dr Marois treat many boys and men with complications of balanitis. Balanitis (inflammation of the glans) and balanoposthitis (inflammation of the foreskin) are common problems in children and uncircumcised men. Balanitis refers to inflammation and swelling of the foreskin (the skin that covers the penis) and the tip of the penis (penis glans).
Balanitis or penile swelling usually occurs in uncircumcised men as a result of infection or poor hygiene. Balanoposthitis refers to more severe inflammation or infection of the glans and foreskin.
Balanitis is more common in men with diabetes. In men with diabetes, balanitis is often caused by Candida, a fungal infection. Balanitis can lead to phimosis, a tightening of the foreskin that makes it difficult to remove the foreskin. ( phimosis )

What are the complications of balanitis?
What is the treatment of balanitis?
Good hygiene often leads to the resolution of balanitis. Balanitis can be treated with medications such as antibiotics or antifungal medications (pills or cream).
If balanitis does not respond to medication or comes back, circumcision may be a good option to prevent the recurrence of child or adolescent balanitis and adult.
What is the effectiveness of circumcision in the treatment of balanitis?
Sometimes, balanitis is severe enough that antibiotics or antifungal medications do not work well. In this situation, circumcision can be performed with a slightly increased risk of wound infection.
In diabetics, better control of diabetes before circumcision is best, as the risk of wound infection and poor healing increases with poorly controlled diabetes.
In general, circumcision cures balanitis in more than 90% of men.


