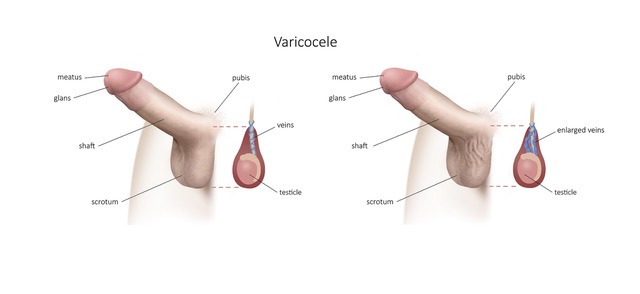

What is varicocele
Varicocele is characterized by the dilation of a vein (varicose) in the spermatic cord, a fibrous cord located in the scrotum above each testicle.
The varicocele occurs mainly on the left side. Venous return of the left testicle is drained to the renal vein, while the venous return of the right testicle is drained to the vena cava. The pressure of the vena cava is lower than in the renal vein.
It is quite common and benign. However, a varicocele can affect men of any age (15%). Its incidence is even higher among men with fertility problems, it could have an impact on fertility.
What are the causes of a varicocele?
The pathophysiology of varicocele is not clearly understood. It seems that there is a malfunction of the unidirectional valves that allow the venous return of the testicles to the heart. Venous blood back flows , accumulates and creates a dilation of the veins in the spermatic cord.
What is the evolution and possible complications of a varicocele?
- In the vast majority of men, a varicocele has no effect on erectile function and sexuality and does not cause any discomfort or problem.
- When it is large, it can cause a feeling of heaviness or pain that may increase over time.
- It can also affect the development and function of the testis with testicular atrophy and, presumably, fertility problems. Thus, 35% of men with primary infertility have varicocele, 80% with secondary infertility, compared with only 15% in the general population.
- It seems that varicose veins could cause, by blood sastagnation, a warming of the testicle which is harmful to spermatogenesis. The wrong venous return could also lead to stagnation of toxic substances, such as tobacco, in the bloodstream, with an impact on spermatogenesis. The reflux of adrenal and renal metabolites could also affect sperm production.
- Note, however, that a man with a varicocele may also have no fertility problem.
- When it is large, it can cause a feeling of heaviness or pain that may increase over time.
- It can also affect the development and function of the testis with testicular atrophy and, presumably, fertility problems. Thus, 35% of men with primary infertility have varicocele, 80% with secondary infertility, compared with only 15% in the general population.
- It seems that varicose veins could cause, by blood sastagnation, a warming of the testicle which is harmful to spermatogenesis. The wrong venous return could also lead to stagnation of toxic substances, such as tobacco, in the bloodstream, with an impact on spermatogenesis. The reflux of adrenal and renal metabolites could also affect sperm production.
- Note, however, that a man with a varicocele may also have no fertility problem.
What are the symptoms of a varicocele?
Most often, varicocele is asymptomatic and causes no discomfort. It is Increased with standing or physical exertion, especially over long periods. It can worsen over the course of a day, It usually relieved when lying on your back.
It often remains unrecognized. It is often discovered by chance or during a fertility test.
Sometimes the varicocele is manifested by an increase in the volume of the testicle, a feeling of heaviness in the left scrotum, sometimes even pains accentuated during prolonged standing, during physical exertion or in hot weather.
It often remains unrecognized. It is often discovered by chance or during a fertility test.
Sometimes the varicocele is manifested by an increase in the volume of the testicle, a feeling of heaviness in the left scrotum, sometimes even pains accentuated during prolonged standing, during physical exertion or in hot weather.
How to make the diagnosis of a varicocele?
The diagnosis is clinical: by palpation and visual examination, or a varicose dilatation above the testicles. In case of doubt, a scrotal ultrasound is performed to confirm the presence of varicocele and rule out any other. The images will reveal unusually large veins and blood stagnation.
What is the treatment of a varicocele?
- No treatment is needed for most men who have a mild symptomatic varicocele.
- In cases of fertility disorders, a consensus exists, in case of clear varicocele associated with abnormalities of spermogram, the treatment of varicocele is recommended.
- There is an embolization treatment of spermatic veins. It is carried out only in certain specialized centres by an interventionist radiologist. Under local anaesthesia and under ultrasound control, a small catheter is introduced into the femoral artery to the dilated spermatic veins. Small metal springs are introduced.
- There is also varicocele cure under microscopy to directly ligate the spermatic veins. This surgical treatment is generally very effective.
- In cases of fertility disorders, a consensus exists, in case of clear varicocele associated with abnormalities of spermogram, the treatment of varicocele is recommended.
- There is an embolization treatment of spermatic veins. It is carried out only in certain specialized centres by an interventionist radiologist. Under local anaesthesia and under ultrasound control, a small catheter is introduced into the femoral artery to the dilated spermatic veins. Small metal springs are introduced.
- There is also varicocele cure under microscopy to directly ligate the spermatic veins. This surgical treatment is generally very effective.


